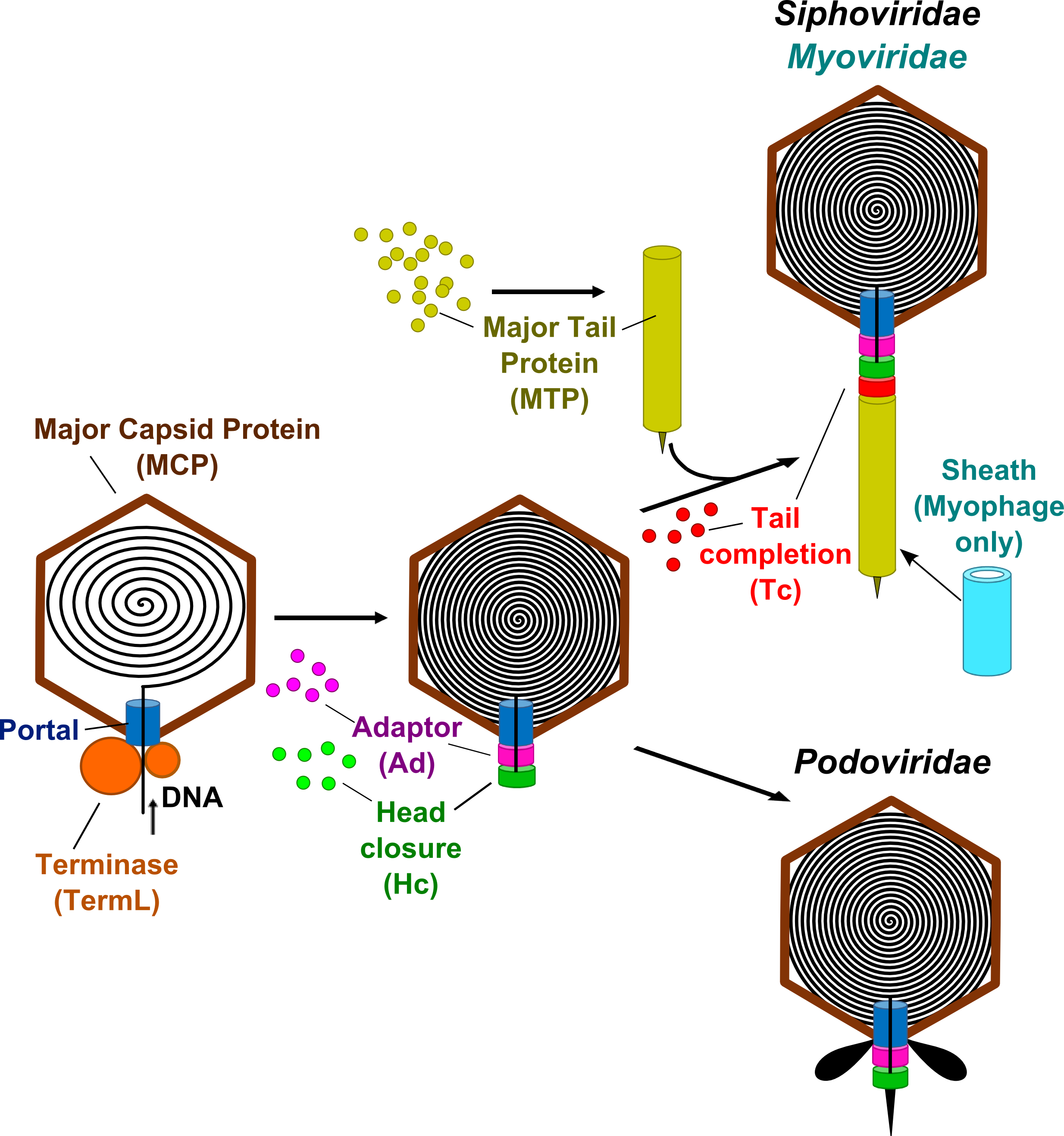
Major Capsid Protein (MCP): protein which self-assembles to form the icosahedral protein lattice called the procapsid.
Portal:
forms a ring-shaped dodecamer through which the DNA is thought to enter
into the procapsid. The portal dodecamer provides the docking point for
an ATPase complex called terminase.
Terminase (TermL):
consists in a heterodimer (a catalytic component with ATPase and
endonuclease activities and a DNA-recognition component that are also
called the large and small subunits respectively). It forms the
packaging motor that translocates the viral dsDNA to the procapsid
interior through the central portal channel.
Adaptor (Ad): is a head-completion protein that belongs to the connector and participates to the portal channel closure. The adaptor protein is directly bound to the portal dodecamer.
Head-closure (Hc): is a head-completion protein that belongs to the connector and participates to the portal channel closure. The head-closure protein is directly bound to the adaptor protein and provides the docking point for tail attachment.
Tail completion (Tc): belongs to long tails and provides the docking interface between the siphophages and myophages pre-assembled long tails and the connector.
Major Tail Protein (MTP): forms the phage's tail tube.
Sheath (only in Myophages):
component of the contractile tail that surrounds the central tail tube
protein. Upon infection, the sheath protein contracts enabling the tail
tube protein to penetrate the cell membrane and then to inject the
genetic material into the host.